Embryo-Transfer
Rückgabe der "Eizelle"
Die Rückgabe der befruchteten Eizelle erfolgt idealerweise am fünften Tag der Embryonalentwicklung (Blastozysten-Stadium), was jenem Zeitpunkt entspricht, an dem ein Embryo bei natürlicher Fortpflanzung vom Eileiter in die Gebärmutter gewandert ist und sich dann einnistet (siehe "Blastozystenkultur").
1. Ablauf
2. "Single Embryo-Transfer"
3. Hormonelle Begleitmedikation
1. Ablauf
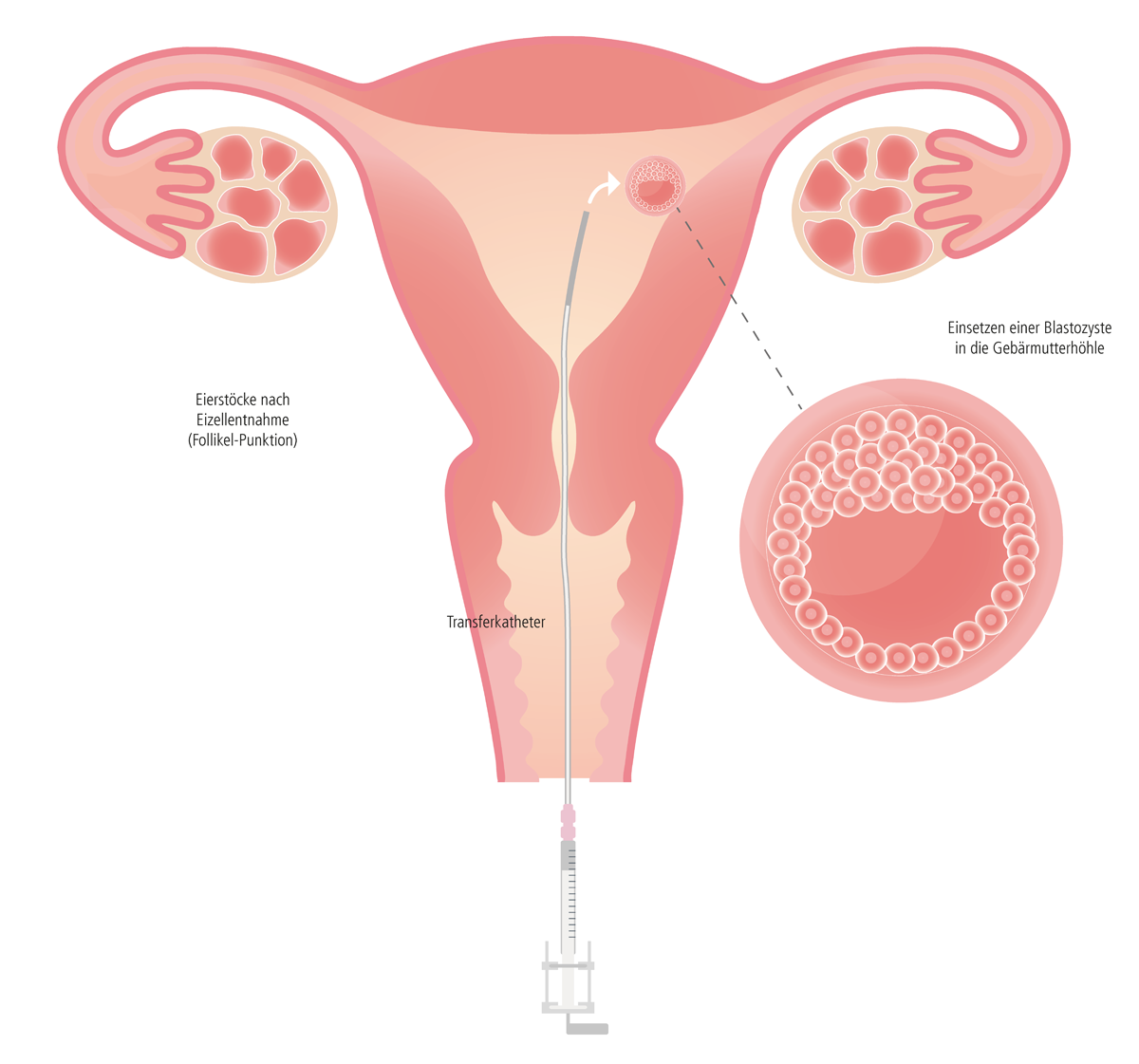
Mit einem dünnen und biegsamen Kunststoffschlauch (Katheter) wird der Embryo durch die Scheide (Vagina) und den Muttermund (Cervix uteri) vorsichtig in die Gebärmutter (Uterus) eingebracht. Dieser Vorgang dauert nur wenige Minuten und verläuft im Allgemeinen schmerzlos. Nach dem Embryo-Transfer bleibt die Frau einige Minuten in Rückenlage liegen und kann anschließend nach Hause entlassen werden.
│ © 2021 Next Fertility IVF Prof. Zech
Einnistung des Embryos
Die Einnistung des Embryos in der Gebärmutter (Implantation) ist ein sehr komplexer Vorgang, der nicht aktiv unterstützt oder gar erzwungen werden kann. Medizinisch gesehen heißt das, man kann lediglich versuchen, mit wissenschaftlich erprobten Methoden, die Gegebenheiten zu verbessern. So wird bei der Rückgabe des Embryos darauf geachtet, dass der Embryo 0,5 - 1 cm unterhalb des höchsten Punktes der Gebärmutterhöhle eingesetzt wird. Es ist erwiesen, dass sich ein Embryo an dieser Stelle einnisten sollte. Diese Kenntnis setzt eine exakte Messung der Gebärmutterlänge voraus, denn die Beschaffenheit der Geschlechtsorgane kann von Frau zu Frau recht unterschiedlich sein. Zudem ist es wichtig, mittels individuell abgestimmten Stimulationsplans, den richtigen Aufbau der Gebärmutterschleimhaut hormonell bestmöglich zu unterstützen. Auch eine entsprechende Lebensweise der Frau kann dabei helfen, die Einnistung des Embryos zumindest nicht zu stören. Eine stressige Abreise nach dem Embryo-Transfer oder ruckartige Bewegungen (schnelles und schweres Heben von Lasten) sollten vermieden werden. Aber auch Langstreckenflüge sind nicht empfehlenswert. Außerdem hat Rauchen oder ein übermäßiger Konsum von Alkohol negative Auswirkungen.
Schwangerschaftstest
Der Schwangerschaftstest im Urin kann zwei Wochen nach dem Embryo-Transfer gemacht werden. Die verordneten Medikamente laut Therapieplan weiternehmen. Auf keinen Fall eigenmächtig absetzen. Sowohl bei einem positiven als auch negativen Schwangerschaftstest sollte uns das Paar im IVF-Zentrum kontaktieren. In Folge wird das weitere Vorgehen besprochen, z.B. Termin zur Blutabnahme, weitere Medikamenteneinnahme, der nächste Kontrolltermin etc.
2. "Single Embryo-Transfer"
Um die Risiken und Folgen (für Mutter und Kind) einer möglichen Mehrlingsschwangerschaft zu minimieren, richten wir in unseren IVF-Zentren die Behandlung danach aus, möglichst einen sogenannten "Single Embryo-Transfer" durchzuführen. Das bedeutet, im Vorfeld optimale Bedingungen zu schaffen, damit nur ein Embryo mit höchstem Einnistungspotential transferiert wird. Dazu gehören viel Erfahrung, optimierte Stimulationsprotokolle, eine individuell abgestimmte Medikation sowie der Einsatz modernster Labortechniken.
3. Hormonelle Begleitmedikation
Um den Zeitraum der Follikel-Punktion wird für einige Tage ein Antibiotikum gegeben, damit das Infektionsrisiko so gering wie möglich gehalten wird, vor allem aber auch deswegen, um beim Transfer nicht evt. vorhandene Keime in die Gebärmutterhöhle "hinaufzuschieben". Nach der Follikel–Punktion und dem anschließendem Embryo-Transfer muss die bei einer künstlichen Befruchtung natürlich auftretende Gelbkörperschwäche (Corpus Luteum Insuffizienz), durch Progesteron-Gaben korrigiert werden und zwar bis zum Nachweis einer positiven Herzaktion. Anschließend wird Progesteron intravaginal bis zur 12ten Schwangerschaftswoche weiter verabreicht. In manchen Fällen ist es sinnvoll, die Medikation noch länger in die Schwangerschaft fortzuführen. Diese Medikation sollte individuell mit dem behandelnden Geburtshelfer abgestimmt werden. Zusätzlich dazu muss Östrogen in Tablettenform (Progynova) ebenfalls für eine gewisse Zeitdauer eingenommen werden (auch wenn erhöhte Östrogenwerte nach einer Stimulation natürlicherweise vorhanden sind). Nur so kann eine Maximierung des Erfolgs erreicht werden. Bei Schilddrüsen–Unterfunktion sollten die gesamte Schwangerschaft hindurch Schilddrüsen–Medikamente in Tablettenform (Eltroxin, L-Thyroxin, Euthyrox) eingenommen werden (Details mit dem/der behandelnden GynäkologIn besprechen). Eventuell sind zusätzliche Medikamente erforderlich, um das Risiko und die Folgen einer Überstimulation (OHSS) zu minimieren (Clexane s.c., Parlodel). Individuell könnten auch andere Medikamente verschrieben werden (Cortisol, Thrombo ASS, Metformin). Eine genaue Beschreibung der verordneten Medikamente erhält jedes Paar in Form eines Merkblattes und eines individuell abgestimmten Therapieplanes.
Tipps und Hilfe nach dem Transfer
Nun beginnt eine äußerst emotionale Zeit, mit vielen unterschiedlichen Gefühlen – bis man endlich weiß, ob es geklappt hat und danach in der Schwangerschaft, wenn man Angst hat, etwas falsch zu machen.
Keine Sorge, es gibt nützliche Tipps und Hilfestellungen: