Stimulation
Follikel-Stimulation
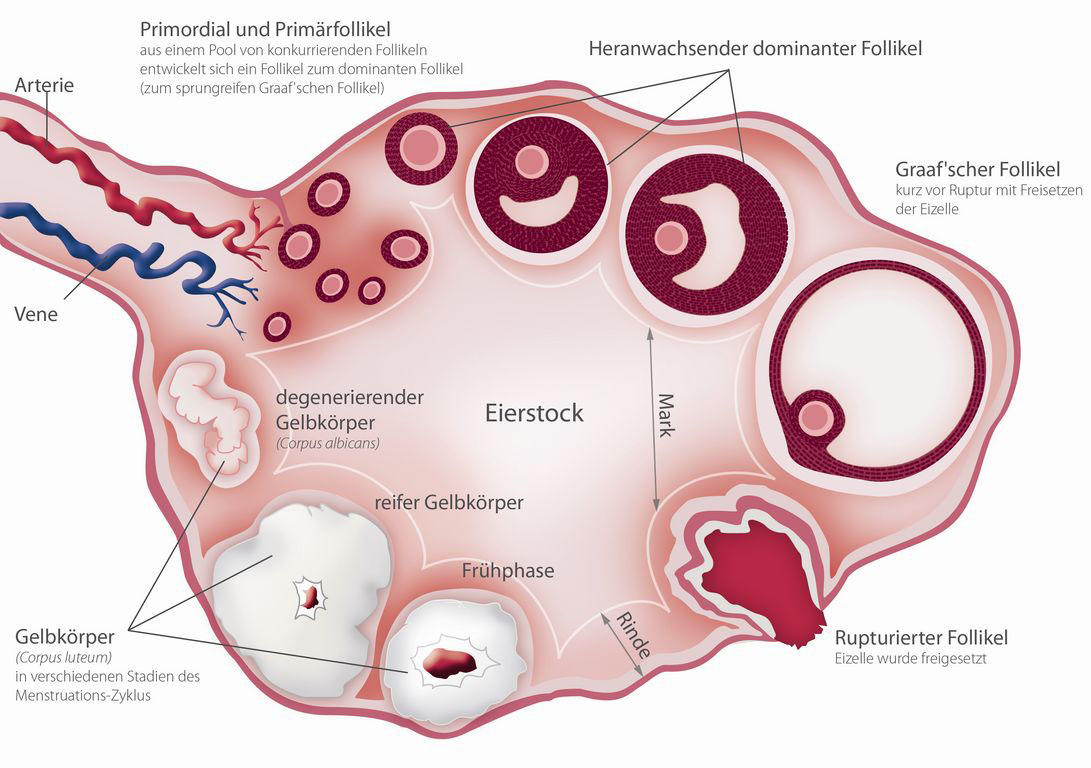
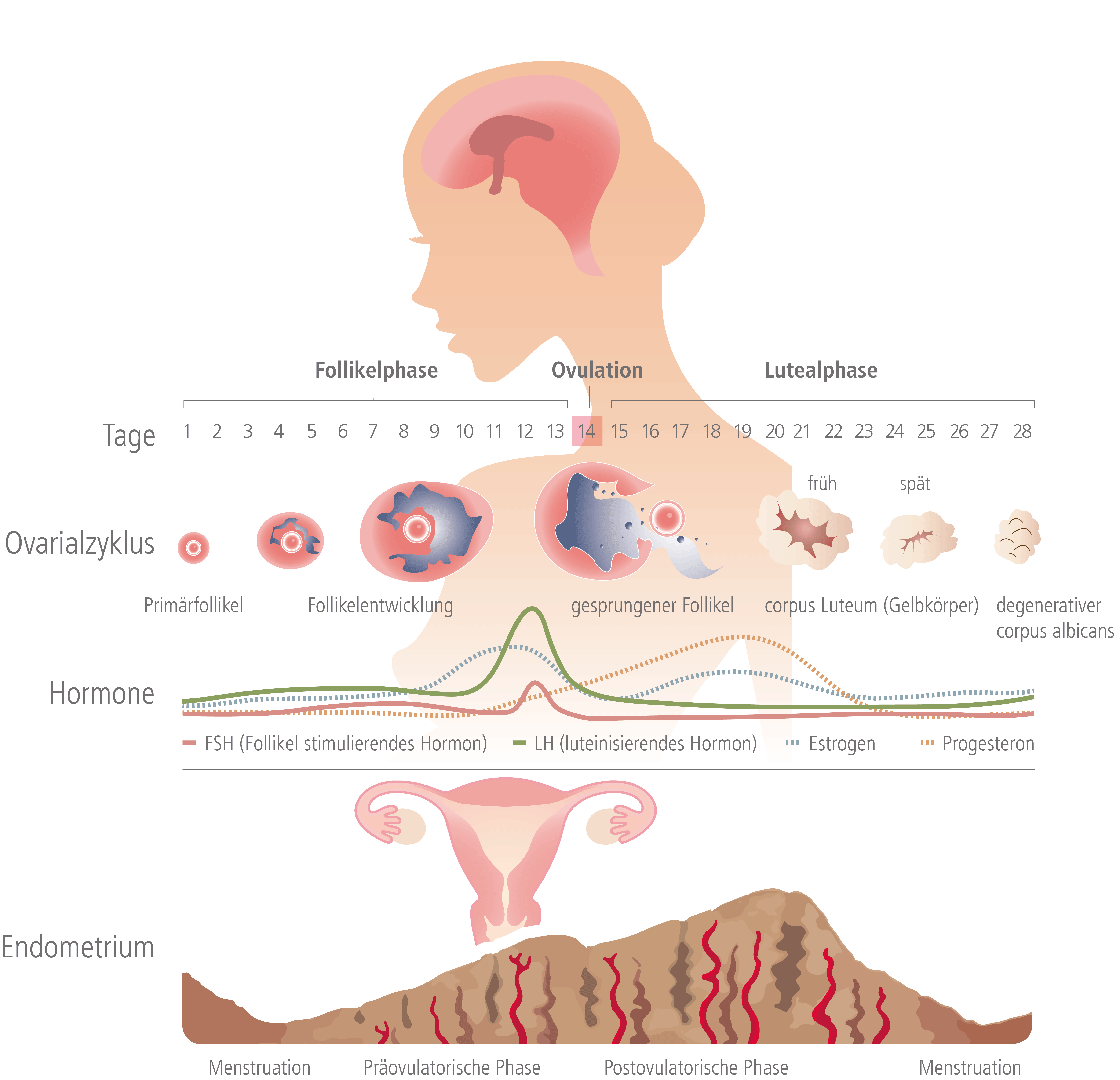
Normalerweise reift im Zyklus der Frau monatlich jeweils eine Eizelle heran
(Follikelwachstum / Eierstock). Im Durchschnitt konkurrieren dabei jedesmal 10 Follikel um die Dominanz. Nur ein Follikel wird zum Leitfollikel mit der reifen Eizelle. Genau hier setzt die hormonelle Stimulation an: Die Frau muss entsprechende Hormone einnehmen (z.B.: Gonadotropine = Hypophysenhormone), damit möglichst viele dieser sonst nicht zur Dominanz kommenden Follikel weiter wachsen, und darin Eizellen heranreifen können.
Hier kann auch beruhigend angemerkt werden, dass eine Frau durch die hormonelle Stimulation der Follikel nicht, wie fälschlicherweise häufig angenommen, vorzeitig in die Wechseljahre kommt.
1. Hormonbehandlung
2. Stimulationsplan
3. Einnahme der Medikamente
4. Ultraschall-Kontrolle
5. Video-Tutorials
1. Hormonbehandlung
Die Follikel-Stimulation bedarf einer entsprechenden Vorbereitung. Zum einen müssen spezielle Hormonwerte im Blut bestimmt werden. Zum anderen erfolgt mittels Ultraschalluntersuchung der sogenannte "Antrale Follikel Count" AFC (= Anzahl der im Ultraschall sichtbaren kleinen Follikel). Außerdem wird die Gebärmutter untersucht, um genaue Kenntnis über die Lage der Eierstöcke zu erlangen und ob z.B. Muskelknoten oder Polypen erkennbar sind. Auf Basis der Hormonwertbestimmung, des "Antralen Follikel Counts" und der Ultraschalluntersuchung der Gebärmutter wird die Stimulierbarkeit der Frau beurteilt.
Damit gezielt Follikel (in denen sich die Eizellen befinden) im Eierstock heranreifen, sollten für eine bestimmte Zeit verschiedene Medikamente bzw. Hormone eingenommen werden. Je nachdem, ob eine Intra-Uterine Insemination (das bedeutet Transfer von Samen, auch Spermien genannt, in die Gebärmutterhöhle) oder aber auch eine Eizellentnahme durch Follikel-Punktion (mit anschließender Befruchtung der Eizellen mit den Samenzellen im Reagenzschälchen) geplant ist, werden unterschiedliche Follikel-Stimulationsprotokolle verwendet. Zur medikamentösen Stimulation der Eierstöcke werden meistens Hormone verwendet, die auch der Körper einsetzt (Gonadotropine). Diese Hormone werden zum größten Teil als Injektion entweder in den Muskel (d.h. intramuskuläre) oder unter die Haut (d.h. subkutan/subcutan) verabreicht (→ siehe "3. Einnahme der Medikamente").
2. Stimulationsplan
Vor und während der Behandlung ist das Kinderwunschpaar oftmals mit vielen Eindrücken und Informationen konfrontiert. Manchmal kann dies verwirrend sein, oder gar Ängste hervorrufen, eventuell etwas falsch zu machen. Besonders bei der Stimulation, welche das Paar, nach der entsprechenden Aufklärung und Unterweisung im IVF-Zentrum, zu Hause selbst durchführt. Denn die Behandlung kann nur dann fortgesetzt werden, wenn die Stimulation erfolgreich war, sprich wenn Eizellen vorhanden sind, die mit den Spermien des Partners befruchtet werden können. Daher muss die Hormontherapie sehr genau umgesetzt werden. Dies wird anhand eines individuell festgelegten Stimulationsplans gewährleistet. Hier weiß das Paar genau was, wann und wie verabreicht werden muss. Zudem können Video-Tutorials zur korrekten Vorbereitung und Injektion der Medikamente sehr hilfreich sein (→ siehe "5. Video-Tutorials").
3. Einnahme der Medikamente
Die Eierstöcke der Frau werden mit der gezielten Gabe von Hormonen stimuliert. Hierfür gibt es verschiedene Medikamente, welche diese Hormone beinhalten. Jene Hormonpräparate, die mittels Spritze verabreicht werden müssen, sind je nach Medikament auf unterschiedliche Weise zu injizieren: in den Muskel (Intramuskuläre Injektion) und/oder unter die Haut (Subkutane Injektion).
Persönliche Erfahrung
"Als ich erfahren habe, dass ich mir selbst die Spritzen setzen muss, da war mir ein bisschen unwohl. Es wurde mir aber erklärt, dass die gewünschte Wirkung eigentlich nur über Spritzen zu erreichen ist. Sie haben mir gezeigt wie das geht und in paar Tagen ist es auch schon wieder vorbei."
"Starke Frau, starker Weg"
2018 setzte die Profiboxerin Nicole Wesner ihr Vertrauen in uns und unsere jahrelange Erfahrung. Von Beginn an war für sie auch wichtig, ihre Geschichte erzählen zu können. So hat sich die 41-jährige getreu ihrem Motto „Wenn Du etwas tust, dann tue es mit Deinem ganzen Herzen“ für diesen Weg der Offenheit entschieden und möchte allen Frauen, die in ähnlichen Situationen sind, Mut machen.
Intramuskuläre Injektion (i.m.)
Als intramuskuläre Injektion bezeichnet man das Einbringen eines flüssigen Arzneimittels in einen Skelettmuskel mittels Spritze und Kanüle. Medikamente, die Sie intramuskulär injizieren sollten sind folgende: Gonadotropine (z.B. Merional, Menogon, Menopur), Humanes Choriongonadotropin (z.B. Pregnyl (A, CH) = Predalon (D), Brevactid, Gonasi), Progesteron (z.B. Agolutin, Gestone, Prontogest, Progesteron Streuli)
Injektionsnadeln:
Zum Auflösen des Medikaments verwenden Sie die Nadeln 18G / 1,2 x 40mm.
Zur intramuskulären Injektion verwenden Sie die grüne Nadel 21G / 0,8 x 40mm.
Durchführung der intramuskulären Injektion:
- Bestimmung des Injektionsortes
- Herstellen der Injektionslösung (bei Trockensubstanzen z.B. Merional, Fostimon, Menogon, Menopur, Pregnyl etc): Das Medikament befindet sich in der Trockensubstanz, die Flüssigkeit dient als Lösungsmittel. Spritzen Sie die Flüssigkeit in die Trockensubstanz, diese löst sich sofort auf und kann wieder in die Spritze aufgezogen werden. Verwenden Sie bitte jeweils die gleiche Anzahl Ampullen mit Flüssigkeit bzw. Trockensubstanz, z.B. 3 Trockensubstanzen mit 3 Flüssigkeiten auflösen.
- Desinfektion der Punktionsstelle
- Einwirkzeit des Desinfektionsmittels abwarten (ca. 30-60 Sekunden)
- Injektionsnadel wechseln (zur Injektion grüne Nadel verwenden, Nadel und Kanüle fest zusammenstecken!)
- zügig senkrecht Einstechen (90°) - Kanüle NICHT ganz einführen, langsam injizieren!
Subkutane Injektion (s.c.)
Der Begriff subkutan steht für eine anatomische Ortsangabe, die sich auf das Gewebe "unter der Haut" bezieht. Diese Unterhaut besteht im Wesentlichen aus dem unmittelbar unter der Haut liegenden Binde- und Fettgewebe. Medikamente, die Sie subkutan injizieren sollten sind folgende: GNRH-Agonist und -Antagonist (z.B. Decapeptyl, Orgalutran, Cetrotide), Gonadotropine (z.B. Puregon, Gonal F, Fostimon)
Injektionsnadeln:
Zum Auflösen des Medikaments verwenden Sie die Nadeln 18G / 1,2 x 40mm.
Zur subkutanen Injektion verwenden Sie die kurze Nadel 27G / 0,40 x 20mm. Bei Puregon und Gonal-F mittels Pen sind eigene Nadeln vorhanden (z.B. 29G / 0,33 x 12mm oder BD Micro-Fine Pen-Nadel)
Durchführung der subkutanen Injektion:
- Bestimmung des Injektionsortes: Sie können entweder in die Bauchdecke unterhalb des Nabels oder am Oberschenkel injizieren. Um zu gewährleisten, dass die Injektion im Subkutangewebe und nicht im Muskelgewebe erfolgt, wird eine Hautfalte gebildet und in diese injiziert. Die Injektion kann in einem Winkel von 45°-90° erfolgen.
- Herstellen der Injektionslösung: bei Trockensubstanzen siehe Punkt 1.2 bei der intramuskulären Injektion. Teilweise sind die Injektionen schon als fertige Injektionslösungen vorhanden. Für Puregon oder Gonal-F gibt es eigene Pen’s zur Verabreichung: siehe Gebrauchsinformation (Packungsbeilage)
- Desinfektion der Punktionsstelle
- Einwirkzeit des Desinfektionsmittels abwarten (ca. 30-60 Sekunden)
- Injektionsnadel wechseln (zur Injektion graue Nadel verwenden, Nadel und Kanüle fest zusammenstecken!) / für Puregon und Gonal F Pens 29G / 0,33 x 12mm bzw. BD Micro-Fine Pen-Nadel
- Zügig in 45° Winkel einstechen, Spritzenstempel zurückziehen und langsam injizieren.
4. Ultraschall-Kontrolle
Um das Follikelwachstum zu überprüfen (Follikel-Monitoring) verwenden wir modernste 3-D Ultraschallverfahren, zur präzisen und automatisierten Vermessung der Follikel. Damit lassen sich Volumen und Größe der heranreifenden Follikel und auch deren Reifegrad exakter analysieren als mit konventionellen Ultraschalltechniken. Es konnte wissenschaftlich belegt werden, dass jene Eizellen, die bei Follikelpunktionen nach 3D-Ultraschall-Überwachung gewonnen wurden, eine höhere Befruchtungsrate aufweisen. Diese Ultraschall-Kontrolle erfolgt in regelmäßigen Abständen über den gesamten Zeitraum der Stimulationsphase. Ziel ist es, den optimalen Zeitpunkt für die Gabe des Auslöse-Hormons HCG und die anschließende Follikel-Punktion zu ermitteln.